Standard
Constant-Mass Doped Flames
For
details on the flame conditions, thermal boundary conditions,
flowrates and mole fractions, and burner dimensions, click here.
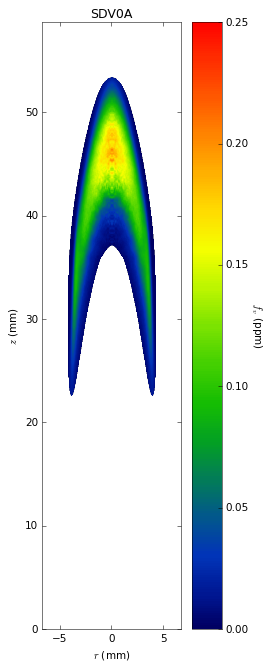
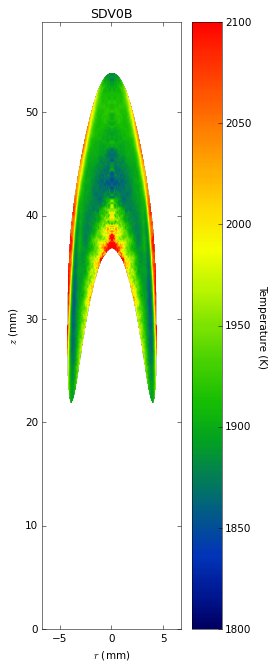
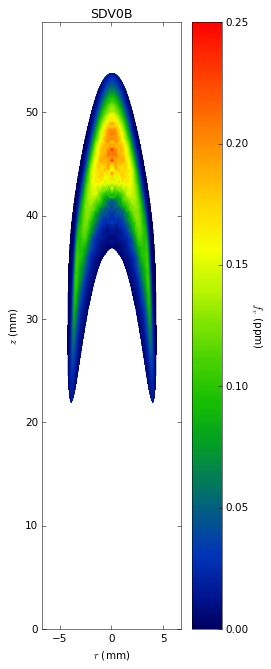
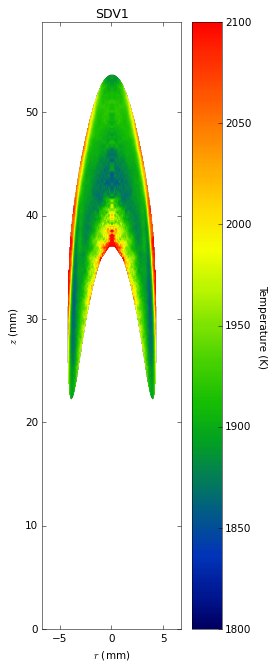
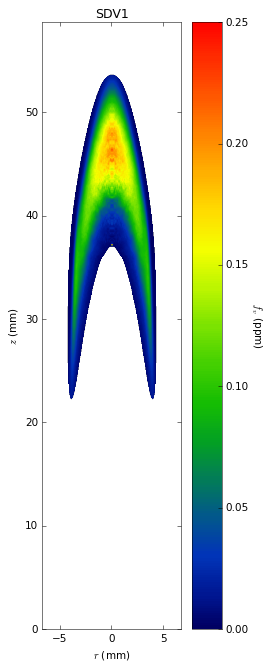
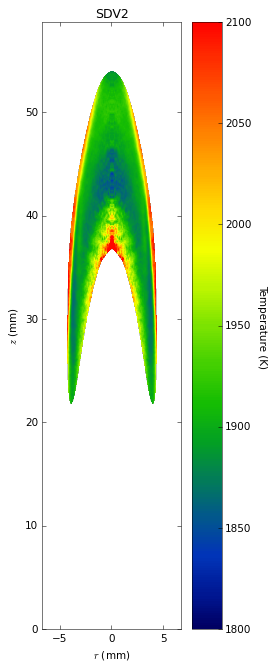
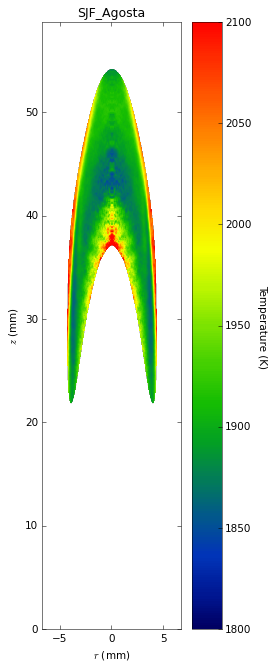
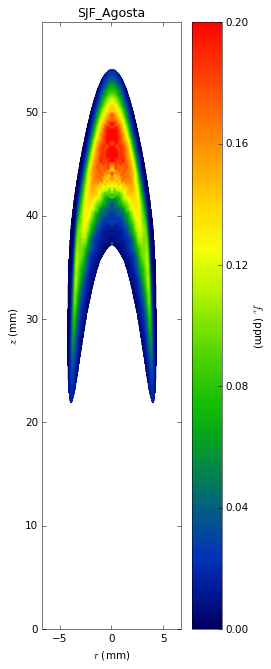
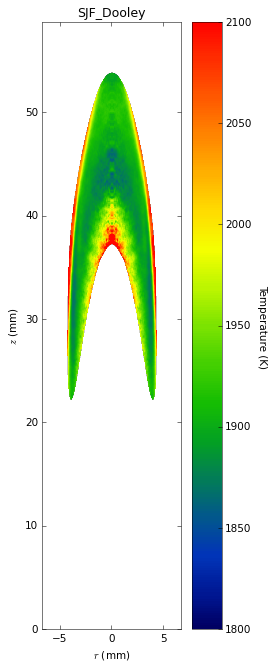
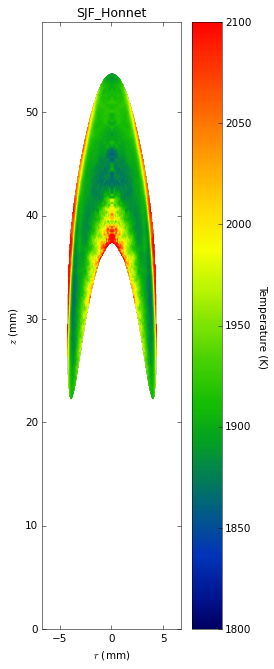
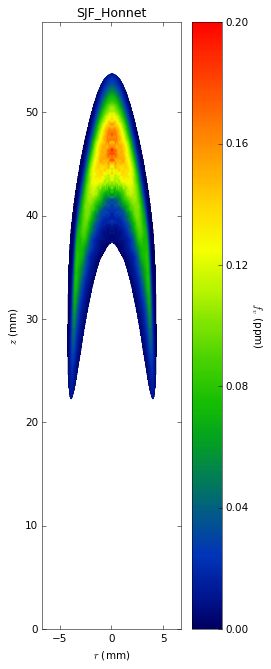
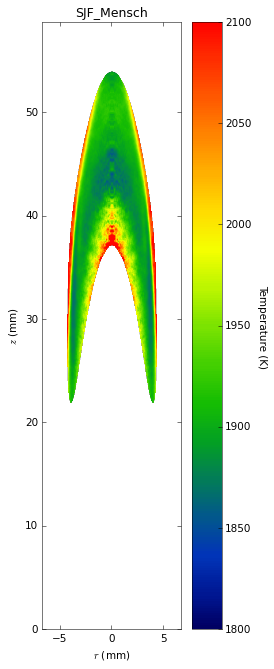
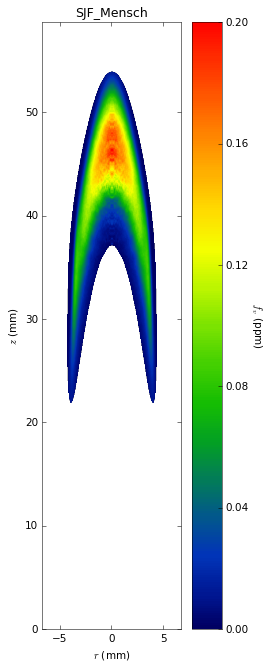
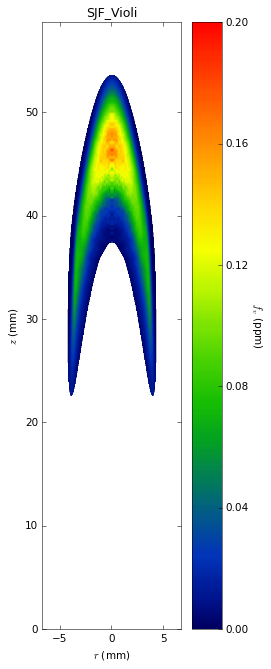
Soot temperatures and volume fractions are based on color ratio
pyrometry using a Nikon D90 camera. Data was published in Ref. **.
Here, soot optical properties were assumed to be constant throughout
the flame with the emissivity varying with wavelength to the -1.38
power.
The data is in a tab delimited, formatted text file, consisting of a
two-dimensional array of floating point values. The data array size is
1668 x 383. The matrix represents an image with pixel spacing of 0.035
mm (28.412 pixels/mm). The first element of the matrix corresponds to
the value in the upper left corner of the images shown. This type of
data can be read in directly to Matlab using the
load
command, or to Python using the
numpy.loadtxt
command.
Use the following table to navigate directly to the surrogate fuel or
compound of interest.
- C. J. Mueller, W. J. Cannella, T. J. Bruno, B. Bunting, H. D.
Dettman, J. A. Franz, M. L. Huber, M. Natarajan, W. J. Pitz, M. A.
Ratclif, and K. Wright, “Methodology for formulating diesel
surrogate fuels with accurate compositional, ignition-quality, and
volatility characteristics,” Energy and Fuels, vol. 26, no.
6, pp. 3284–3303, 2012.
- A. Agosta, N. P. Cernansky, D. L. Miller, T. Faravelli, and E.
Ranzi, “Reference components of jet fuels: Kinetic modeling and
experimental results,” Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,
vol. 28, no. 7, pp. 701–708, 2004.
- S. Dooley, S. H. Won, J. Heyne, T. I. Farouk, Y. Ju, F. L. Dryer,
K. Kumar, X. Hui, C. J. Sung, H. Wang, M. A. Oehlschlaeger, V. Iyer,
S. Iyer, T. A. Litzinger, R. J. Santoro, T. Malewicki, and K.
Brezinsky, “The experimental evaluation of a methodology for
surrogate fuel formulation to emulate gas phase combustion kinetic
phenomena,” Combustion and Flame, vol. 159, no. 4, pp.
1444–1466, 2012.
- S. Honnet, K. Seshadri, U. Niemann, and N. Peters, “A surrogate
fuel for kerosene,” Proceedings of the Combustion Institute,
vol. 32 I, no. 1, pp. 485–492, 2009.
- A. Mensch, R. J. Santoro, T. A. Litzinger, and S.-Y. Lee, “Sooting
characteristics of surrogates for jet fuels,” Combustion and
Flame, vol. 157, pp. 1097–1105, 2010.
- A. Violi, S. Yan, E. G. Eddings, A. F. Sarofm, S. Granata, T.
Faravelli, and E. Ranzi, “Experimental formulation and kinetic model
for JP-8 surrogate mixtures,” Combustion Science and Technology,
vol. 174, no. 11-12, pp. 399–417, 2002.